Department for Energy Security and Net Zero has published the statistical report on the UK energy trends for the 1st quarter of 2023.
Renewable generation reached a record share of 47.8 per cent of total generation, up from 5.8 per cent in the same quarter of 2010. Renewable generation was boosted with a new offshore wind record of 19.2 per cent up
from 0.6 per cent in the same quarter of 2010.
Final consumption of energy dropped on the same period last year. On an adjusted basis that reflects seasonal and temperature trends, industrial consumption was down 11 per cent, and consumption by households down by 9.5 per cent continuing the recent run of lower consumption figures that have accompanied increased energy and other household costs. Transport demand increased by 9.0 per cent, with increases in road and particularly
aviation fuel use.
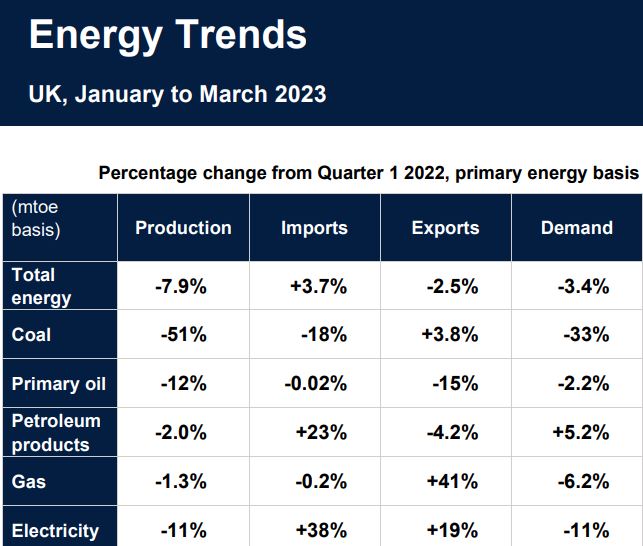
Energy production fell on the same period last year, mainly due to continued low oil production which has not fully recovered since the extensive maintenance carried out in the summer of 2021. Nuclear output hit a record low, down 22 per cent on the same quarter last year due to outages in all plants, and reduced capacity compared to the same time last year.
Trade continues to differ from recent norms. Gas exports to Europe remain high as the UK continues to support European markets as they move away from Russian gas. Electricity imports into the UK reached a record high due to pricing differentials, a contrast to last year when the UK was exporting record levels of electricity to help make good European shortfalls. Net import dependency was 43.6 per cent for the quarter up 5.0 percentage points on last
year.
Key headlines of the report are:
- In the first quarter of 2023 total primary energy production was 27.3 million tonnes of oil equivalent, 8.0 percent lower than in the first quarter of 2022.
- Total primary energy consumption for energy uses fell by 2.8 per cent. When adjusted to take account of weather differences, primary energy consumption fell by 2.4 percent.
- Total final energy consumption (excluding non-energy use) was 1.6 percent lower compared to the first quarter of 2022. Transport consumption rose by 8.7 percent, but domestic consumption fell by 7.4 percent, despite slightly colder weather than a year earlier. Industrial consumption fell by 6.8 per cent, and other final users (mainly from the service sector) consumption fell by 2.4 percent. On a seasonally and temperature adjusted basis, final energy consumption fell by 1.9 percent, with a rise in transport, but falls in all other sectors which continues the recent run of lower consumption figures that have accompanied increased energy and other costs.
- Net import dependency was 43.6 per cent in the first quarter of 2023, up 5.0 percentage points on the same
quarter of 2022, with imports at the highest level since the fourth quarter of 2019.
Read the complete report by clicking below: